How to Flush DNS
Why would you need to flush DNS?
The Windows and Linux operating systems will cache IP addresses and DNS records to help you resolve requests more quickly. An example of this is if you search https://openeye.net in your browser, the browser may store it in its local cache storage. When you search the same website URL from there on, it will not have to collect the DNS information from the servers every time you search the URL. The downside to this is that if the cache corrupts, it may resolve some of the symptoms below.
-
Slow search speeds
-
Unable to resolve URLs
-
Unable to access the application
Flushing the DNS cache can improve these symptoms and improve computer security as well.
How to flush DNS (Windows)
-
In windows, type "cmd" in the search bar and press enter to access the Command Prompt.
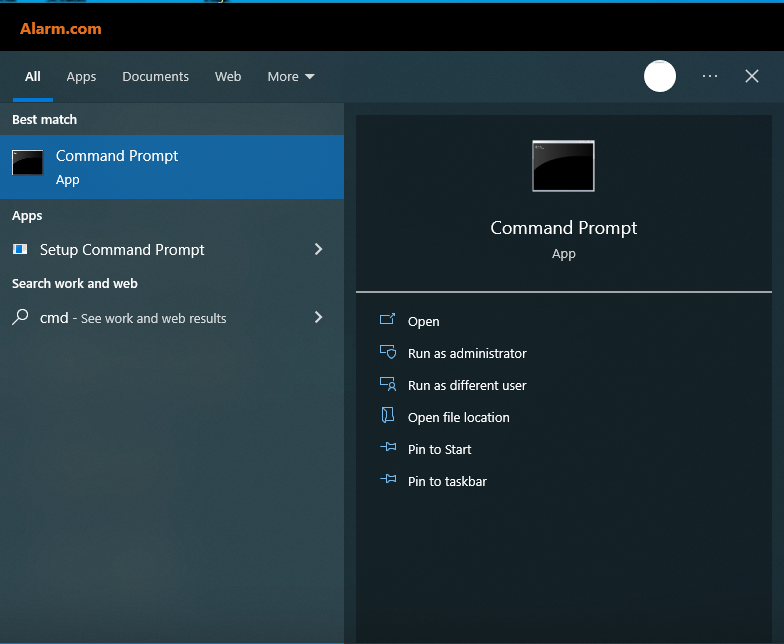
-
Within the Command Line, type ipconfig /flushdns and press enter.
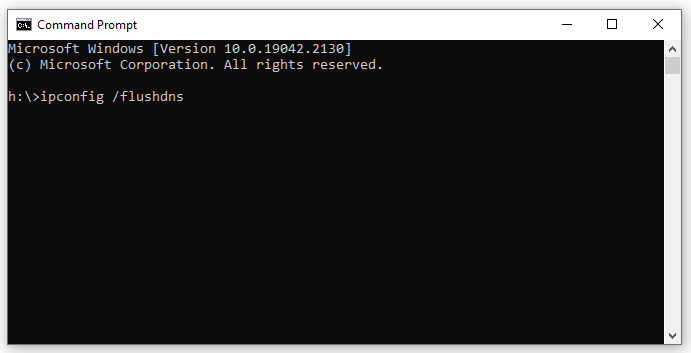
-
DNS has been flushed.
How to flush DNS (Linux recorders)
-
Launch support tools to access the Linux desktop NOTE: You will need to be on the console of the recorder.
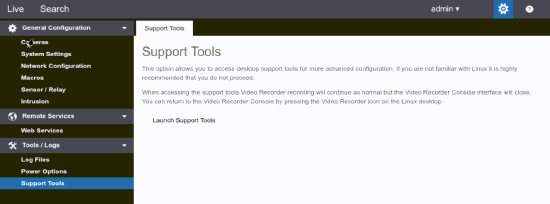
-
Launch Web Browser
-
Type chrome://net-internals/#dns and press enter
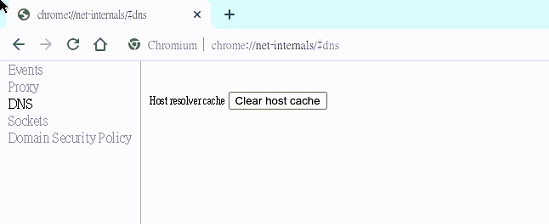
-
Click Clear host cache
-
DNS has been flushed.
