What is APIPA?
What is APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing)?
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) is a feature in operating systems that enables computers or recorders (DHCP client) to automatically self-configure an IP address and subnet mask when their DHCP server isn’t reachable. The IP address range for APIPA is 169.254.0.1-169.254.255.254, with the subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
When a DHCP client boots up, it looks for a DHCP server in order to obtain network parameters. If the DHCP client can’t communicate with the DHCP server, it uses APIPA to configure itself with an IP address from the APIPA range. This way, the host will still be able to communicate with other hosts on the local network segment that are also configured for APIPA.
Consider the following example:
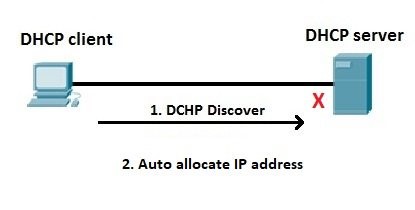
The host on the left is configured as DHCP client. The host boots up and looks for DHCP servers on the network, this could be a server or a router. If the DHCP server is down or inaccessible and can’t respond to the host or does not connect an APIPA address is assigned. After some time (from a couple of seconds to a couple of minutes, depending on the operating system) the client auto-configures itself with an address from the APIPA range (e.g. 169.254.154.22).
NOTE
If your host is using an IP address from the APIPA range, there is usually a problem on the network. Check the network connectivity of your host and the status of the DHCP server (router).
The APIPA service also checks regularly for the presence of a DHCP server (every three minutes). If it detects a DHCP server on the network, the DHCP server replaces the APIPA networking addresses with dynamically assigned addresses.
